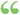 For compressible flow this becomes: where y is the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume... For compressible flow this becomes: where y is the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume...  Science - Page 66edited by - 1883Full view Science - Page 66edited by - 1883Full view - About this book
 | Chemical Society (Great Britain) - 1918 - 666 pages
...that a strict following of the law is impossible. A further formula is deduced for the calculation of the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume. This has the forms k = l + 2C/3cvm and k=l/l-2C/3cpm, in which £=2-98, A = cP/ct>, and m is the molecular... | |
 | Chemical Society (Great Britain) - 1895 - 890 pages
...formula, using the author's experimental results, decreases continuously as the temperature rises : the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume decreases from 0° to + 4°, and then increases continuously up to 35°, the highest temperature at... | |
 | Chemical Society (Great Britain) - 1896 - 1104 pages
...elementary or compound nature of argon, experiments were made on the velocity of sound in it. From these the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume was deduced in the well-known manner. The accuracy of the apparatus used was tested by preliminary... | |
 | American Association for the Advancement of Science - 1899 - 648 pages
..." conductivity of air, X " " constant of radiation according to Newton's law of cooling, and y " " ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume. From ( I ) it is seen that the motion at any point may be considered as the resultant of two simple... | |
 | Chemical Society (Great Britain) - 1915 - 872 pages
...and 3'0 for the diatomic gases and argon respectively, and the corresponding values for the ratio y of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume, 1/4 and T666 respectively. The ignition-points, obtained by means of calculations similar to that on... | |
 | James Clerk Maxwell - 1871 - 344 pages
...place, we find for the ratio of the specific heats, T.^ v.— KAL ' ALE Kv T-A_M y AM E 'AN ' AK or the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume is equal to the ratio of the elasticity when no heat escapes to the elasticity at constant temperature.... | |
 | Frank Salter - 1874 - 134 pages
...reduction of temperature. In every case, such as the above, whatever the expanding gas may be, if 7 be the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume, then it is evident that "i Pi or, using the differential notation, Ap being a decrement. And since... | |
 | 1875 - 410 pages
...carbonic acid, from which constants the heat equivalent may be obtained by the formula the value of — or the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume being 1-3945, as ascertained by M. Kegnault in 1871, by experiments on the velocity of sound in air.... | |
 | ROBERT H. THURSTON - 1876 - 782 pages
...of adiabatic curves for any gas is p — constant X v ^ where y is constant, and has for its value the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure, to that at constant volume, of the gas under consideration. Denoting by CP and CJ, CJ and CJ, the specific heats at constant pressure... | |
 | 1876 - 840 pages
...equation of adiahatic curves for any gas is p = constant XP where y is constant, and has for its value the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure, to that at constant volume, of the gas under consideration. Denoting by C£ and CJ, CJ" and C'', the specific heats at constant... | |
| |