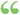 For compressible flow this becomes: where y is the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume... For compressible flow this becomes: where y is the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume...  Science - Page 66edited by - 1883Full view Science - Page 66edited by - 1883Full view - About this book
 | American Association for the Advancement of Science - 1899 - 650 pages
..." conductivity of air, X " " constant of radiation according to Newton's law of cooling, and y " " ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume. From (i) it is seen that the motion at any point may be considered as the resultant of two simple harmonic... | |
 | American Association for the Advancement of Science - 1899 - 646 pages
..." conductivity of air, X " " constant of radiation according to Newton's law of cooling, and y " " ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume. From (i) it is seen that the motion at any point may be considered as the resultant of two simple harmonic... | |
 | Victor von Richter - 1900 - 454 pages
...observed only with other substances at very high temperatures (p. 79)- This is evident from the relation of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume, which in the case of monatomic gases equals 1.67, whereas with polyatomic gases — those built up... | |
 | 1901 - 520 pages
...negligible in this case ; hence The adiabatic gas relation gives p = Cf,y, where C is a constant and f is the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume. - ri I pv dp = \tf. [. _L— Let - -- - = « and /J = — — Ci r r- 1 Expanding and neglecting all... | |
 | Joseph John Thomson - 1903 - 580 pages
...273 + T .. . For in such an expansion pv* is constant, where p is the pressure and v the volume and 7 the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume : but pv = R6, where 0 is the absolute temperature and R a constant, hence we have during an adiabatic... | |
 | Joseph Ames - 1904 - 782 pages
...knowledge of the difference between these two quantities. It may be proved by higher mathematics that the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume equals the ratio of the adiabatic coefficient of elasticity to the one at constant temperature (see... | |
 | Arthur Gordon Webster - 1904 - 605 pages
...principles of thermodynamics give us the relation for adiabatic compression 17) p = l>Q*, where u is the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume, whose numerical value is about 1.4. We then have -< o\ ^ I dp /, .. 97 b^gy'~i 18) 7 = 0* = - / -f... | |
 | Philip Rounseville Alger - 1905 - 160 pages
...neither gains heat from, nor loses it to, other bodies, and in this case pvy = k' = Tivl (where y is the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume for the gas in question, its value being 1.408 for air and practically the same for all gases), and... | |
 | Frederick Converse Beach, George Edwin Rines - 1905 - 1076 pages
...for the several gases in this way, by different observers, are not as accordant as might be desired. The ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume appears to have approximately the following values: Oxygen, 1.40; hydrogen, 141; nitrogen, 1.41; carbon... | |
 | Leander Miller Hoskins - 1906 - 300 pages
...For perfect gases the adiabatic law connecting pressure and density is (5) p2 w2 ^ ' in which k is the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume, and has the value 1.41 very nearly. The work done by unit mass in expanding from pressure pi and density... | |
| |